The Element.getBoundingClientRect() method returns a DOMRect object providing information about the size of an element and its position relative to the viewport.
Bạn đang xem: Top view là gì
Bạn đang xem: Top view là gìThe returned value is a DOMRect object which is the smallest rectangle which contains the entire element, including its padding and border-width. The left, top, right, bottom, x, y, width, and height properties describe the position and size of the overall rectangle in pixels. Properties other than width and height are relative to the top-left of the viewport.
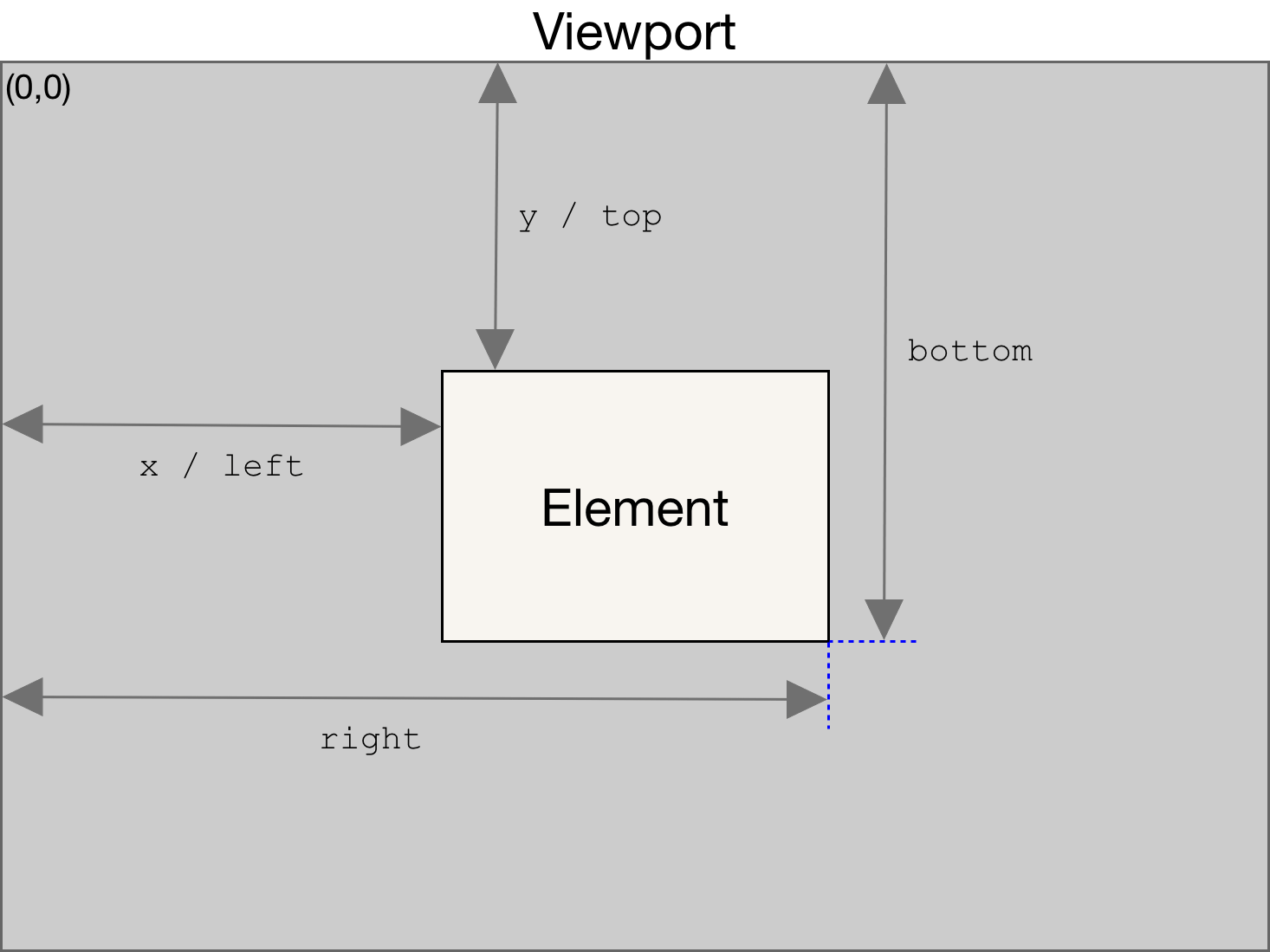
The width and height properties of theDOMRect object returned by the method include the padding and border-width, not only the content width/height. In the standard box model, this would be equal to thewidth or height property of the element + padding+border-width. But ifbox-sizing: border-box is set for the element this would be directly equal to itswidth or height.
The returned value can be thought of as the union of the rectangles returned by getClientRects() for the element, i.e., the CSS border-boxes associated with the element.
Empty border-boxes are completely ignored. If all the element”s border-boxes are empty, then a rectangle is returned with a width and height of zero and where the top and left are the top-left of the border-box for the first CSS box (in content order) for the element.
Xem thêm: Khái Niệm Tổng Quát 100% Về Hàng Thanh Lý Là Gì ? Thanh Lý Là Gì
If you need the bounding rectangle relative to the top-left corner of the document, just add the current scrolling position to the top and left properties (these can be obtained using window.scrollX and window.scrollY) to get a bounding rectangle which is independent from the current scrolling position.
Cross-browser fallback
Scripts requiring high cross-browser compatibility can use window.pageXOffset and window.pageYOffset instead of window.scrollX and window.scrollY. Scripts without access to these properties can use code like this:
// For scrollX(((t = document.documentElement) || (t = document.body.parentNode)) && typeof t.scrollLeft == “number” ? t : document.body).scrollLeft// For scrollY(((t = document.documentElement) || (t = document.body.parentNode)) && typeof t.scrollTop == “number” ? t : document.body).scrollTop
Examples
Basic
This simple example retrieves the DOMRect object representing the bounding client rect of a simple element, and prints out its properties below it.
div>div>The returned DOMRect object can be modified in modern browsers. This was not true with older versions which effectively returned DOMRectReadOnly. With IE and Edge, not being able to add missing properties to their returned ClientRect, object prevents backfilling x and y.
Due to compatibility problems (see below), it is safest to rely on only properties left, top, right, and bottom.
rect = elt.getBoundingClientRect()// The result in emptyObj is {}emptyObj = Object.assign({}, rect)emptyObj = { …rect }{width, …emptyObj} = rectDOMRect properties top,left, right, and bottom are computed using the values of the object”s other properties.







